In the exploration of life sciences, epigenetics has always been a key area for decoding the mysteries of diseases. It has always exuded a mysterious and fascinating charm, attracting countless scientific researchers to continue exploring. The research results that shine in top journals contain deep insights into epigenetics and methylation mechanisms, like a beacon in the long river of academic research, illuminating our way forward. Let us review the classic papers published in top journals such as JAMA and Nature, sort out the context of academic development, appreciate the charm of classic papers, and feel the pioneering spirit of cutting-edge scientists in the field of disciplines.
On July 6, 2022, Yu Wenqiang’s team from the Institute of Biomedical Hospital of Fudan University , in collaboration with the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Fudan University and the Xijing Hospital Affiliated to the Air Force Medical University , identified the third pan-cancer marker SIX6 , and revealed its application in multiple clinical scenarios such as early detection, metastasis risk prediction, and auxiliary surgical margin judgment for lung cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, and urothelial cancer. The related results, “Mutually exclusive epigenetic modification on SIX6 with hypermethylation for precancerous stage and metastasis emergence tracing”, were published in the Nature journal Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. (Original address: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-022-01026-7)
Figure 1. The pan-cancer marker SIX6 was published in the Nature journal Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
Yu Wenqiang’s team at Fudan University has previously published a number of important results on pan-cancer markers, including the first pan-cancer marker HIST1H4F published in Cancer Res (IF=13.312) , the official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, in 2019, the second pan-cancer marker PCDHGB7 published in the internationally renowned journal Clinical and Translational Medicine (IF=11.492) in 2021, and the application of the pan-cancer marker PCDHGB7 in the early screening of endometrial cancer in the international academic journal Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences (IF=6.113) in 2022. One marker, one test, simple and accurate, with unlimited imagination in application scenarios, pan-cancer markers have great potential!
Early cancer screening is the only way to defeat tumors
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the world. In 2020, there were approximately 19.29 million new cases of cancer worldwide, and approximately 10 million people died from cancer. Cancer is the leading cause of death in China. In China, there were approximately 4.57 million new cases and 3 million deaths in 2020, accounting for approximately 23.7% and 30.2% of the total global cancer incidence and mortality in that year. For almost all cancers, if they can be detected, diagnosed and treated in the early stages , their chances of survival will be greatly improved. However, due to factors such as “inherent defects in existing diagnostic and treatment methods, economic costs, and availability of medical resources”, approximately 50% of cancers are already in the late stages when diagnosed, and the survival rate of advanced malignant tumors is low . Therefore, early cancer screening and timely intervention can effectively block cancer progression and reduce morbidity and mortality.
Existing screening methods, including imaging tests and endoscopic screening, often have a certain lag in the time of tumor occurrence. Early tumor screening based on molecular markers has received increasing attention in recent years, but its application in clinical practice also faces some problems . On the one hand, there is an urgent need to explore more effective molecular markers; on the other hand , the vast majority of existing markers are only targeted at specific tumor types, and there are few reports on markers that can be used for screening of multiple cancers . Yu Wenqiang’s team at Fudan University has been deeply engaged in tumor marker research and has discovered a series of pan-cancer markers, which enables one marker to be used for the detection of multiple tumors in multiple clinical scenarios , pushing the research and application of tumor methylation markers to a new level.
Figure 2. Previous report on pan-cancer markers in Science and Technology Daily
The third pan-cancer marker discovered: SIX6
Abnormal DNA methylation is a key event in the occurrence of cancer. Studies have found that tumors have low methylation in the whole genome sequence and abnormal high methylation at specific sites. The high methylation of these specific sites can be used for early screening of tumors. In addition, DNA methylation also has inherent advantages in terms of detection stability and specificity, but there are many bottlenecks and barriers in sequencing technology and price in practical applications. In response to this, Yu Wenqiang’s team at Fudan University previously constructed the “Guide Positioning Sequencing” technology (GPS) for whole genome DNA methylation detection, achieving a major breakthrough in accuracy and coverage. Using this technology, the research team discovered HIST1H4F , a site that is highly methylated in multiple cancer types , proposed the concept of “whole cancer marker” and proved the potential clinical application value of high methylation of HIST1H4F in lung cancer detection. After that, the research team identified the second pan-cancer marker PCDHGB7 after arduous searches and used it for early detection of cervical cancer. The pan-cancer marker can advance cervical cancer screening to the high-grade squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (HSIL) stage, truly achieving “cancer prevention” before “cancer”.
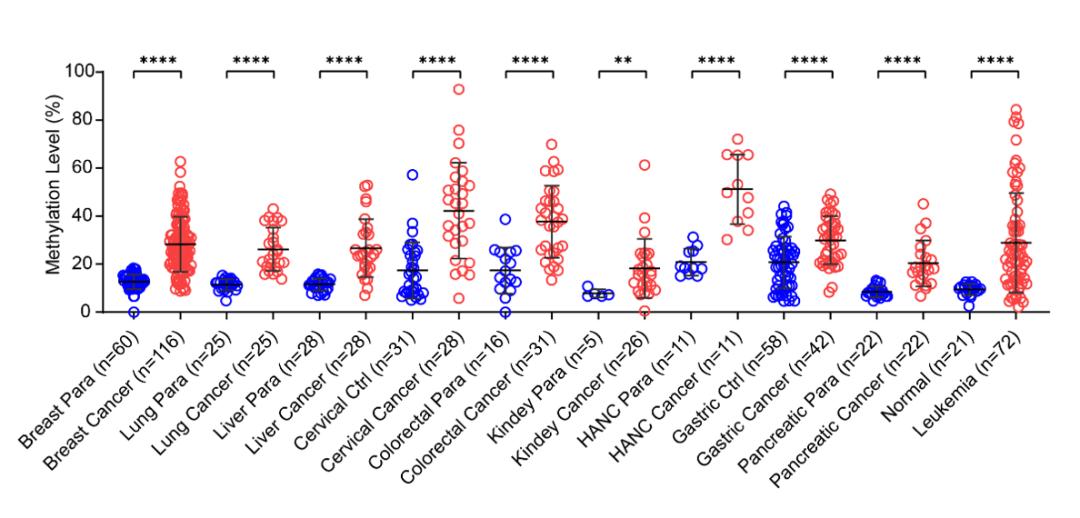
While continuing to explore the application potential of previous pan-cancer markers, the research team discovered another differentially methylated region in tumor cells. Among them , the SIX6 gene has attracted special attention. In addition to its traditional role in tissue formation and organ development, it also plays a tumor regulatory function by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. The research team verified it in 7010 samples of 15 cancer types from the TCGA sample library and found that high methylation of the SIX6 site in tumor samples is universal. Furthermore, by collecting 678 clinical samples of 10 common tumors, it was once again proved that high methylation of SIX6 is another new pan-cancer marker.
Figure 3. SIX6 is highly methylated in tumors as a pan-cancer marker
Pan-cancer markers locate tumor detection in the pre-cancer stage, from a daydream to a dream come true
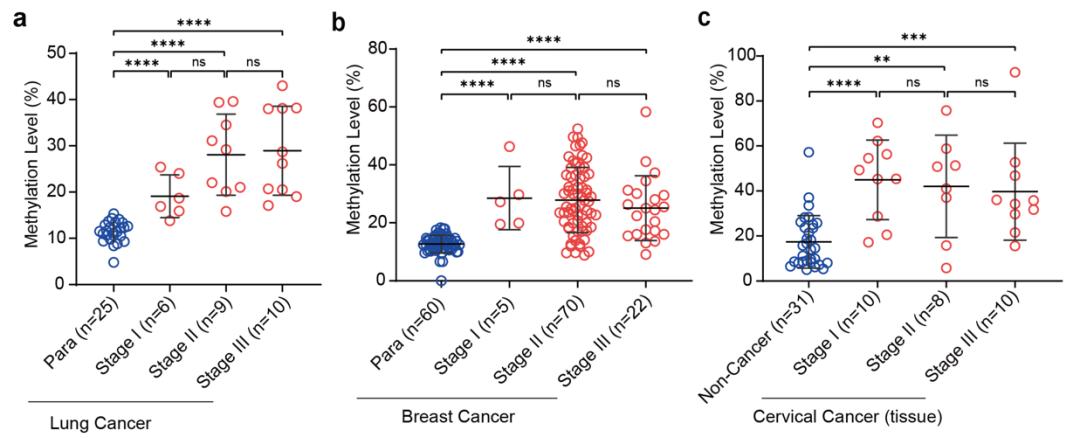
The key to early cancer screening is “early”. How early does the hypermethylation of SIX6 appear? In the TCGA database samples with clear staging, the research team found that the hypermethylation of SIX6 in 12 tumors all appeared in stage I (localized cancer), and treatment at this stage also corresponds to a higher survival rate and a better prognosis. Subsequently, it was confirmed in clinical samples that the hypermethylation of SIX6 appeared in the early stages of lung cancer, breast cancer, and cervical cancer, and was also stable in the subsequent stages of cancer development. This shows that SIX6 is suitable for full-process monitoring of multiple cancer types .
Figure 4. Hypermethylation of SIX6 appears in the early stages of cancer
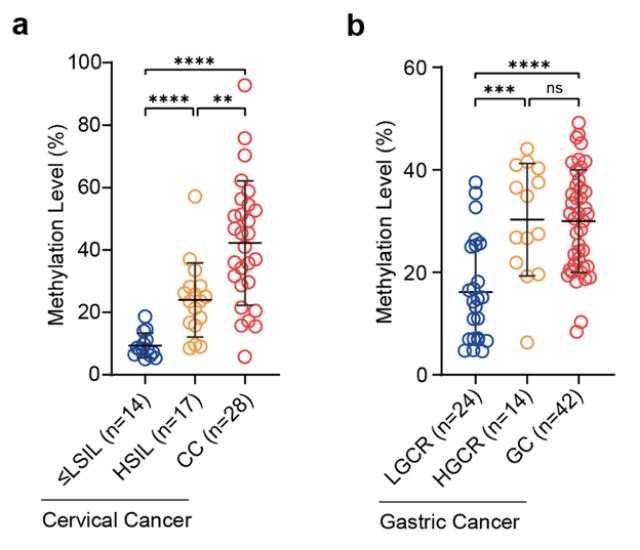
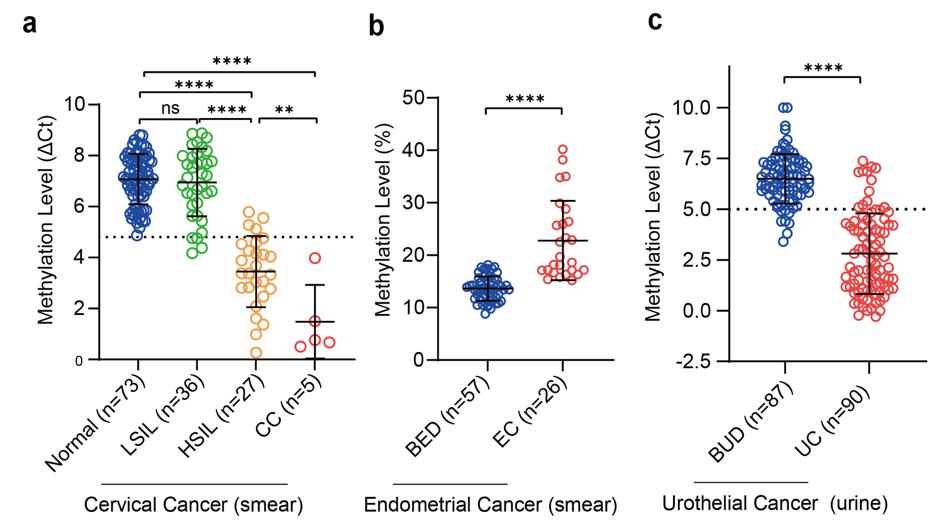
In view of the characteristics of long-term evolution of tumors, the research team further explored whether the high methylation of SIX6 could be earlier on the timeline of tumor development. To this end, the research team selected cervical cancer and gastric cancer samples with staged progression characteristics and found that compared with low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL), SIX6 showed a significant high methylation level in the high-grade squamous intraepithelial neoplasia stage (HSIL) like cervical cancer (CC); and compared with low gastric cancer risk (LGCR, including chronic non-atrophic gastritis, gastritis and superficial gastritis) samples, high gastric cancer risk (HGCR, including atrophic gastritis and HSIL) samples and gastric cancer also showed higher SIX6 methylation levels. This shows that the high methylation of SIX6 is a very early event in tumor progression, and may serve as an important feature of the transformation of normal cells to precancerous cells, and the application of this feature is expected to advance “cancer prevention” to the “pre-cancer” stage . In order to make the selection more user-friendly for the clinical screening application group, the research team selected non-invasive cervical smears and urine samples, and verified that high methylation of SIX6 occurs in the early stage of cervical cancer – high-grade squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (HSIL) stage, and can significantly distinguish endometrial cancer from benign endometrial disease (BED) and urothelial carcinoma from benign urothelial disease (BUD), and has good sensitivity and specificity, which has a great time advantage in clinical early screening.
Figure 6. SIX6 hypermethylation is significantly different in non-invasive samples
Catch the thief of tumor metastasis, and remove the tumor under the shadowless lamp.
At present, 20%-30% of cancers have already progressed to the intermediate stage (regional cancer) when they are discovered. Cancer cells spread to nearby lymph nodes, tissues or organs, and metastasis becomes a key factor affecting the choice of treatment strategy and prognosis. Preliminary verification found that the high methylation of SIX6 appeared earlier, so can the high methylation of SIX6 be used for the “early” judgment of tumor metastasis? The research team detected the methylation level of SIX6 in cancer lymph nodes during the potential metastasis stage of breast cancer and found that SIX6 was also in a high methylation state in the lymph nodes of positive metastasis samples, while it was significantly reduced in lymph node metastasis-negative samples. This shows that the methylation detection of SIX6 has great potential and advantages in tracking the “early metastasis” of cancer, so that the choice of breast cancer treatment methods no longer depends on experience, but on scientific and precise policy implementation. In addition, in tumor resection surgery, it is the common wish of every doctor and patient to “remove the tumor with your hands”. The determination of the surgical margin of the tumor directly determines the prognosis of the tumor. After all, no one wants to “put something under the tumor” during surgery. The research team’s analysis of gastric cancer surgical margin samples showed that the SIX6 methylation level in the surgical margin was higher than that in the control normal samples, indicating that SIX6 hypermethylation at the molecular level may occur earlier than the gold standard based on pathological judgment. Using SIX6 hypermethylation as an indicator of precision surgery and prognosis prediction is extremely time- and cost-effective .
Figure 7. SIX6 methylation can be used as an indicator for tumor metastasis and resection margin
Although tumors are highly heterogeneous, precision medicine based on tumor heterogeneity is just in time. However, the continuous expansion of the common characteristics of tumors will definitely help the scientific and medical communities better understand the overall picture of tumors, and the common characteristics of tumors based on pan-cancer markers will surely become an important direction for future tumor research . Simplifying complex problems is undoubtedly one of the important ways to solve problems. The emergence of pan-cancer markers allows tumor research to explore the intrinsic essence of tumors through the appearance of heterogeneity, and the study of the common characteristics of tumors will greatly promote tumor research. Preventing cancer before it occurs is no longer a matter of paper talk, and lowering the incidence of tumors in Chinese people is no longer a dream. With pan-cancer markers in hand, there is no need to worry about not being able to tie up the dragon!
Post time: Jun-12-2025